Suretyship sometimes referred to as surety insurance is a term used to describe the relationship between three parties: the principal debtor, the creditor, and the surety. The surety is the individual or company who guarantees the payment of a debt or performance of an obligation in the event the principal debtor fails to do so.
In other words, the surety becomes responsible for the debt or obligation if the principal debtor fails to fulfill their responsibilities. Suretyship is commonly used in business transactions, such as loans, leases, contracts, and other forms of credit. The creditor may require a surety as an additional safeguard to ensure that they receive payment or performance of the obligation.
Suretyship can also be used in legal proceedings, such as bail bonds, where a surety guarantees the appearance of the defendant in court. There are different types of surety bonds that can be used in various situations.
One common type of surety bond is a performance bond, which guarantees that a contractor will complete a project according to the terms of the contract. If the contractor fails to fulfill their obligations, the surety will step in and complete the project or compensate the creditor for any losses.
Another type of surety bond is a payment bond, which guarantees that the contractor will pay their subcontractors, suppliers, and laborers for their work on the project.
The surety is not an insurer; they do not assume the risk of the obligation like an insurance policy. Instead, the surety is a guarantor who provides a guarantee of the principal debtor’s performance.
If the principal debtor fails to fulfill their obligation, the surety becomes responsible for the debt or obligation. The surety can seek reimbursement from the principal debtor, but ultimately they are responsible for the payment or performance of the obligation.
When a surety guarantees an obligation, they must be confident in the principal debtor’s ability to fulfill their responsibilities. The surety will typically conduct an investigation into the principal debtor’s financial situation, credit history, and ability to perform the obligation before agreeing to provide a guarantee. The surety may also require collateral or a personal guarantee from the principal debtor to reduce their risk.
Suretyship can be a valuable tool for businesses and individuals who need to guarantee the payment or performance of an obligation. However, it is important to understand the risks involved and to work with a reputable surety company. Choosing the wrong surety company or agreeing to an unreasonable guarantee can have serious financial consequences.
Suretyship is a legal concept that allows individuals and businesses to guarantee the payment or performance of an obligation. The surety becomes responsible for the obligation if the principal debtor fails to fulfill their responsibilities.
There are different types of surety bonds that can be used in various situations, and it is important to work with a reputable surety company to minimize the risks involved. Overall, suretyship is a valuable tool for protecting the interests of both creditors and debtors in various transactions.
Read Also: Navigating the Complex World of Truck Insurance
Surety bonds
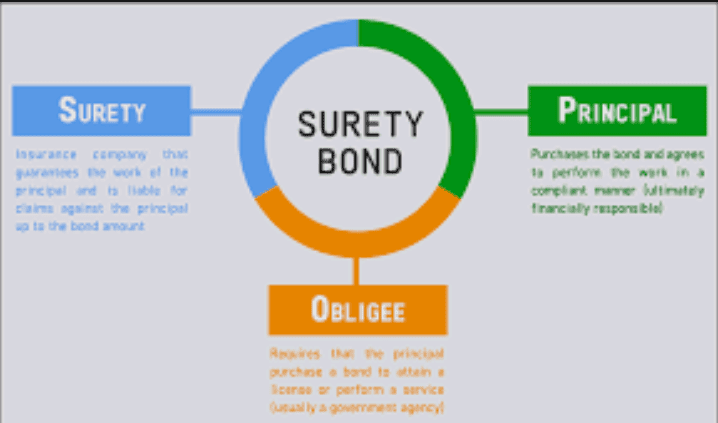
Surety bonds are an important part of many industries, providing financial security and peace of mind to both contractors and their clients.
A surety bond is a contract between three parties: the principal (the contractor or business owner who is required to purchase the bond), the obligee (the person or organization who requires the bond), and the surety (the company that issues the bond and guarantees payment if the principal fails to meet their obligations).
There are several different types of surety bonds, each designed to serve a specific purpose. Performance bonds are the most common type of surety bond and are typically required on construction projects. A performance bond guarantees that the contractor will complete the project as agreed upon in the contract.
If the contractor fails to complete the project or fails to meet the agreed-upon quality standards, the surety will step in to ensure that the project is completed or that the obligee is compensated for any damages incurred.
Payment bonds are another type of surety bond often required in the construction industry. These bonds ensure that subcontractors and suppliers are paid for their work or materials, even if the general contractor fails to make payment.
This provides an additional layer of protection for those working on the project, ensuring that they will receive payment for their work even if the primary contractor fails to meet their obligations.
Another type of surety bond is a license bond, which is required for certain professions and businesses. These bonds ensure that the business or professional in question will follow all applicable laws and regulations in their industry, and provide financial compensation to any clients or customers who are harmed by the business’s actions.
Fidelity bonds are another type of surety bond, which provide protection against employee theft or dishonesty. These bonds are typically purchased by businesses that handle large amounts of cash or valuable assets, such as banks, casinos, or jewelry stores.
Surety bonds are an important tool for protecting businesses and individuals in a variety of industries. By providing financial security and ensuring that obligations are met, surety bonds help to build trust and confidence in business transactions.
If you’re a contractor or business owner, it’s important to understand the different types of surety bonds and how they can benefit you and your clients. By working with a reputable surety company, you can ensure that you have the protection you need to operate your business with confidence and peace of mind.
Payment Bonds
Payment bonds are a type of surety bond that provides protection for subcontractors, suppliers, and laborers who work on construction projects. These bonds are issued by a surety company and guarantee that the contractor will pay all of their bills related to the project.
In the construction industry, payment bonds are often required on public projects to ensure that everyone who works on the project is paid for their work. Private owners may also require payment bonds to protect themselves from potential liens and legal action from unpaid subcontractors and suppliers.
There are several parties involved in a payment bond, including the contractor, the surety company, and the obligee. The obligee is typically the project owner or the government agency that is funding the project. The contractor is the party who is responsible for paying their bills, and the surety company provides the bond.
When a subcontractor or supplier is hired to work on a project, they will typically request a copy of the payment bond to ensure that they are protected if the contractor fails to pay them. If the contractor does not pay their bills, the subcontractor or supplier can file a claim with the surety company to receive payment.
HiIn order to file a claim on a payment bond, the subcontractor or supplier must provide proof of their work on the project and the amount that they are owed. The surety company will then investigate the claim and determine if it is valid. If the claim is approved, the surety company will pay the subcontractor or supplier directly.
There are several benefits to using payment bonds on construction projects. First and foremost, payment bonds ensure that everyone who works on the project is paid for their work. This helps to prevent disputes and legal action that can delay the project and increase costs.
Payment bonds also provide protection for the project owner. If a subcontractor or supplier files a lien against the property, it can be difficult to sell or finance the property until the lien is resolved. Payment bonds prevent liens from being filed and ensure that the project owner can sell or finance the property without any issues.
Payment bonds are an important tool in the construction industry that provide protection for subcontractors, suppliers, and laborers who work on construction projects.
They ensure that everyone is paid for their work and prevent disputes and legal action. If you are working on a construction project, it is important to understand payment bonds and how they can protect you.
Read Also: A Guide to Commercial Insurance
Bail Bonds

Bail bonds are an important aspect of the criminal justice system. They are a form of financial security that is provided by a third-party, usually a bail bondsman, to ensure that a defendant appears in court for their trial. In this article, we will explore the concept of bail bonds, how they work, and their implications for the justice system.
What are Bail Bonds?
Bail bonds are a type of financial guarantee that is used to secure the release of a defendant from jail while they await trial. When a person is arrested and charged with a crime, they are typically held in jail until their trial.
However, in some cases, the defendant may be released on bail. Bail is a sum of money that the defendant must pay to the court as a guarantee that they will show up for their trial. If the defendant appears in court as scheduled, the bail money is returned to them. However, if they fail to appear, the bail money is forfeited to the court.
In some cases, defendants are unable to pay the full amount of their bail. This is where bail bonds come in. A bail bondsman, also known as a bail agent, is a person or company that provides a guarantee to the court that the defendant will appear in court as scheduled.
The bail bondsman charges the defendant a fee, typically 10% of the total bail amount, and then posts the full bail amount with the court. If the defendant fails to appear in court, the bail bondsman is responsible for paying the full amount of the bail to the court.
How do Bail Bonds Work?
When a defendant is unable to pay their bail in full, they may turn to a bail bondsman for assistance. The defendant pays the bondsman a non-refundable fee, typically 10% of the total bail amount, and the bondsman provides a bond to the court for the full amount of the bail.
The defendant is then released from jail on the condition that they appear in court for their trial.
If the defendant fails to appear in court as scheduled, the bondsman has a limited amount of time to locate the defendant and return them to court. If the defendant cannot be located, the bondsman is responsible for paying the full amount of the bail to the court. The bondsman may use a bounty hunter to locate the defendant if necessary.
If the defendant appears in court as scheduled, the bail money is returned to the bondsman, and the defendant is no longer under any obligation to the bondsman.
Implications of Bail Bonds
Bail bonds have both positive and negative implications for the justice system. On the one hand, they allow defendants who are unable to pay their bail in full to be released from jail while they await trial.
This can be beneficial for defendants who have a strong case and are not considered flight risks. It also allows defendants to continue working and supporting their families while they await trial.
However, bail bonds also have negative implications. The fees charged by bail bondsmen can be expensive, and defendants who are unable to pay them may be forced to remain in jail.
This can create an unequal system where wealthier defendants are able to secure their release while poorer defendants remain in jail. Additionally, bail bonds can create a financial burden for defendants and their families, who may be forced to take out loans or sell assets to pay the bail bond fee.
Bail bonds are an important aspect of the criminal justice system that allows defendants to be released from jail while they await trial. They can be beneficial for defendants who are unable to pay their bail in full, but they also have negative implications for the justice system.
Ultimately, it is up to lawmakers and the courts to determine the role of bail bonds in the criminal justice system and to ensure that the system is fair and just for all.
Read Also: 30 Awesome DIY Projects that You’ve Never Heard of
