With regards to your dental hygiene also known as oral hygiene, it is very important for us to understand that the teeth is the most important part of your body therefore keeping it healthy and neat is hygienic for your body and health. Early detection and treatment are also very important to effectively manage any common oral condition.
Without proper care for your teeth, you will experience some teeth problems like toothache, tooth decay and many more issues associated with dental hygiene.
Definition of Dental Hygiene (Teeth Care)
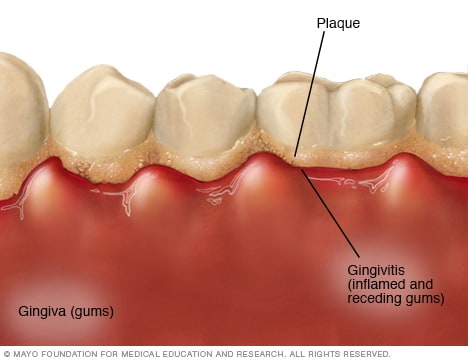
Dental hygiene also called Oral hygiene can also be defined as the practice of keeping one’s mouth clean and free of disease and other problems by regular brushing of the teeth and cleaning between the teeth.
It is important that dental hygiene (oral hygiene) be carried out on a regular basis to enable prevention of dental disease and bad breath.
Dental hygienists lead the way in ensuring the health, function, and maintenance of dental implants.
Read Also: 6 Great Personal Hygiene Tips for Females
The Dimensions of Dental Hygiene
Definition of a Dental Hygienist?
Dental Hygienists are highly trained professionals who are specialists in the field of preventative dental care. Dentists and hygienists work closely together in proactively preventing and controlling dental disease, and to establish and maintain a favourable oral environment to help ensure successful outcomes for past and future treatment.
What do dental hygienists do?
Typically, hygienists will:
- Professionally clean your teeth so that you feel confident and healthy about your teeth and smile.
- Apply topical fluoride to your teeth to strengthen and re-mineralize weak areas before these teeth break down with decay.
- Apply agents to your gums and teeth to help reduce and control harmful bacterial activity.
- Monitor and screen for gum disease.
- Clean those areas of your mouth that are inaccessible to you, helping to prevent breakdown of these areas.
- Help in the prevention of cavities and gum disease.
- Advise and council patients on correct oral hygiene techniques and practices.
- Advise and council patients on good dietary and supplementary practices.
In addition, some hygienists have received advanced training in areas such as administration of local anaesthesia and the treatment of some gum disorders.
According to a professional, He says….
With the concern about COVID-19, my area recently had something else to be worried about — an outbreak of Legionnaire’s disease. When we return to treating patients, what can I do to prevent this?
One of my patients underwent replacement of occlusal amalgams on #3 and #4 with recurrent decay using a resin restorative material. The patient complained of swelling and bruising the length of her mandible that lasted about 2 weeks, along…
The use of lesser known injections can offer myriad benefits—from improving patient comfort to providing longer lasting pain relief.
The safety of clinicians and patients in the dental office rests on adherence to evidence-based infection control standards.
Knowing when it’s time to replace ultrasonic inserts/tips is integral to successful instrumentation.
Detecting subgingival calculus deposits is key to ensuring periodontal health.
A new technique aims to obtain the cleanest pits and fissures possible, improving sealant effectiveness.
Oral health professionals can help ensure a lifetime of oral health by educating children and families about the importance of diet during the developmental years.
The career paths for dental hygienists continue to expand, providing additional professional opportunities and improving access to care.
Read Also: Importance of Good Personal Hygiene
What do you recommend to patients who want to maintain their oral health but abstain from fluoride?
In light of declining vaccination rates, oral health professionals need to be knowledgeable about current vaccine recommendations so they can best advise their patients and support public health.
Learn how to improve the effectiveness of your power instrumentation during initial periodontal therapy, prophylaxis, and periodontal maintenance.
The following strategies will help oral health professionals prevent and manage infection control exposure events.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, answers or any other contributions? Kindly use the comment box below for all your contributions.
You are also encouraged to kindly share this information with your loved ones if found useful enough as we cannot reach everyone at the same time. Thank you