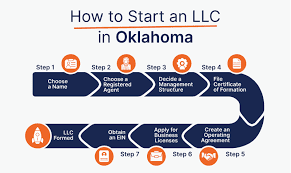
Do you want to know how to start a business in Oklahoma? Here is a guide. Starting a business can be an exciting and rewarding venture, but it also requires careful planning and a solid understanding of the legal and regulatory requirements. If you’re considering launching a business in Oklahoma, you’re in the right place.
In this article, we’ll provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to start a business in Oklahoma, covering essential aspects such as business planning, legal structure, registrations, licenses, and more. So, let’s dive in and explore the process of starting a business in the beautiful state of Oklahoma.
Develop a Business Plan: Before embarking on any business endeavor, it’s crucial to create a comprehensive business plan. This document will serve as your roadmap and help you define your business objectives, target market, products or services, marketing strategy, financial projections, and other essential elements. A well-thought-out business plan will not only guide you but also assist in securing financing from investors or lenders.
Choose a Legal Structure: Selecting the appropriate legal structure for your business is a critical decision. In Oklahoma, common options include Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, Limited Liability Company (LLC), and Corporation. Each structure has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of liability, taxation, and management. Consult with an attorney or a business advisor to determine the most suitable legal structure for your venture.
Register Your Business Name: Choosing an effective and memorable name for your business is essential. Ensure the name you select is unique and doesn’t infringe on any existing trademarks. To register your business name, conduct a name availability search through the Oklahoma Secretary of State website. Once you’ve confirmed availability, you can register your business name by filing the necessary documents and paying the required fees.
Obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN)
An Employer Identification Number (EIN) is a unique nine-digit number issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It is used to identify your business entity for tax purposes. You can obtain an EIN by applying online on the IRS website. This number is required if you plan to hire employees, open a business bank account, or file federal taxes.
Fulfill Tax Obligations: Understanding and fulfilling your tax obligations is crucial for the success and legality of your business. Register with the Oklahoma Tax Commission (OTC) to obtain the necessary permits and licenses for collecting sales tax, withholding income tax, and other applicable taxes. Additionally, familiarize yourself with federal tax requirements to ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
Acquire Business Licenses and Permits: Depending on your business type and industry, you may need to obtain specific licenses and permits to operate legally in Oklahoma. Visit the Oklahoma Business Portal (OBP) or the OTC website to identify the licenses and permits required for your particular business activities. Ensure you complete the necessary applications, pay the associated fees, and comply with any additional regulations.
Secure Financing: If you require funding to start or grow your business, explore various financing options. Oklahoma offers several programs and resources to support small businesses, including loans, grants, and tax incentives. Research and consider options such as Small Business Administration (SBA) loans, local banks, angel investors, venture capitalists, and crowdfunding platforms.
Set Up Business Operations: Establishing your business operations involves securing a physical location, purchasing equipment and inventory, setting up utilities, and hiring employees if necessary. It’s essential to create a productive and safe work environment, comply with zoning regulations, and obtain any required permits for construction or renovations.
Develop a Marketing Strategy: To attract customers and promote your products or services effectively, devise a comprehensive marketing strategy. Identify your target market, study your competitors, and utilize both online and offline marketing channels. Leverage social media platforms, search engine optimization (SEO), content marketing, email marketing, and traditional advertising methods to raise awareness and generate sales.
Starting a business in Oklahoma requires careful planning, compliance with legal requirements, and diligent execution. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll be on your way to establishing a successful business venture. Remember to seek professional advice when needed and continuously adapt your strategies to the changing market dynamics.
Read Also: How to find investors for construction business
Business Plan in Oklahoma

Starting a business can be an exciting and rewarding venture, but it requires careful planning and strategic thinking. A well-crafted business plan serves as a roadmap for success, providing a framework to guide your decisions and actions. If you’re considering launching a business in Oklahoma.
Researching the Market: Before diving into your business plan, it’s crucial to conduct thorough market research specific to Oklahoma. Understand the local economy, industry trends, target audience, and competition.
Idntify your target market’s needs and preferences, and evaluate the demand for your product or service in the region. Gathering this information will help you make informed decisions about your business model, marketing strategies, and pricing.
Defining Your Business: Clearly articulate your business concept, mission, and vision. Describe your products or services, highlighting their unique selling points and how they meet customer needs. Determine your business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, etc.), and outline your legal and operational requirements.
Identifying Your Target Audience: Identify and define your target audience in Oklahoma. Consider factors such as age, gender, income level, interests, and geographic location. This information will guide your marketing efforts and enable you to tailor your products, services, and messaging to resonate with your target market effectively.
Analyzing the Competition: Conduct a thorough analysis of your competitors in Oklahoma. Identify their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. Determine how your business can differentiate itself and offer a unique value proposition.
Highlight your competitive advantages and develop strategies to overcome any challenges posed by existing players in the market.
Creating a Marketing Strategy: Develop a comprehensive marketing strategy to promote your business effectively in Oklahoma. Consider both online and offline channels, such as social media, search engine optimization (SEO), content marketing, print media, local partnerships, and community involvement. Tailor your marketing messages to resonate with the local culture and preferences while ensuring consistent branding across different channels.
Financial Planning: Create a detailed financial plan for your business. Estimate your startup costs, including equipment, inventory, licensing fees, and marketing expenses.
Project your revenue and expenses for at least the first three years, factoring in sales forecasts, operating costs, and anticipated growth. Explore potential funding options, such as loans, grants, or investment opportunities available in Oklahoma.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Familiarize yourself with the legal and regulatory requirements for operating a business in Oklahoma. Register your business entity with the Oklahoma Secretary of State, obtain any necessary permits or licenses, and ensure compliance with tax obligations. Consult with legal and financial professionals to ensure your business meets all legal requirements and remains in good standing.
Operations and Management: Outline your operational processes, including production, supply chain management, staffing, and quality control. Define your organizational structure and roles, identifying key personnel and their responsibilities. Consider any specific workforce development initiatives or incentives available in Oklahoma to attract and retain skilled employees.
Developing a comprehensive business plan is a crucial step towards building a successful enterprise in Oklahoma. By conducting thorough market research, defining your business, understanding your target audience, analyzing the competition, and creating a robust marketing and financial plan, you can lay a strong foundation for your business’s growth and profitability.
Remain adaptable and open to adjustments as you navigate the dynamic business landscape in Oklahoma, staying attuned to emerging trends and opportunities. With careful planning and execution, your business can thrive in the diverse and vibrant Oklahoma market.
Business Permits in Oklahoma
Starting a business in Oklahoma requires careful planning and adherence to various legal requirements. One crucial aspect is obtaining the necessary business permits and licenses.
Understanding the permit requirements specific to your industry and complying with state and local regulations is essential for operating legally and avoiding potential penalties. In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide to business permits in Oklahoma.
Research Your Business Type: Different types of businesses have different permit requirements. Begin by researching the specific permits and licenses applicable to your industry in Oklahoma.
The Oklahoma Secretary of State’s website and the Oklahoma Department of Commerce’s Business Licensing Service are valuable resources for gathering information.
Determine Your Legal Structure: Before applying for permits, determine the legal structure of your business. Common options include sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), and corporation.
Each structure has its own legal and tax implications, so consult with an attorney or a qualified professional to make an informed decision.
Obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN)
An Employer Identification Number (EIN) is required for most businesses and is obtained from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). You can apply for an EIN online through the IRS website. The EIN is used for tax purposes and to identify your business entity.
Register Your Business Name: If you plan to operate your business under a name other than your legal name, you must register a “Doing Business As” (DBA) with the Oklahoma Secretary of State. This applies to sole proprietorships, partnerships, and certain types of corporations. Registering a DBA allows you to conduct business under a different name while maintaining your legal identity.
Obtain State Licenses and Permits: Certain industries in Oklahoma require state-specific licenses or permits. Examples include healthcare-related professions, contractors, real estate agents, and financial institutions. Visit the Oklahoma Department of Commerce website to determine if your business falls into a regulated industry and requires a state license.
Check Local Permit Requirements: In addition to state permits, you may need to obtain local permits and licenses. Local requirements can vary depending on the city or county in which you plan to operate. Contact the local city hall or county clerk’s office to inquire about the specific permits needed for your business location.
Sales Tax Permit: If you plan to sell taxable goods or services, you must register for a sales tax permit with the Oklahoma Tax Commission. This permit allows you to collect sales tax from customers and remit it to the state. You can register online through the Oklahoma Tax Commission’s website.
Professional Licenses: Certain professions in Oklahoma require professional licenses. Examples include doctors, lawyers, accountants, architects, and cosmetologists. If your business falls into a regulated profession, ensure that you and your employees have the necessary professional licenses to practice legally.
Federal and Environmental Permits: Some businesses may require federal permits or certifications, particularly if they are involved in activities such as importing or exporting goods, operating a daycare center, or working with hazardous materials.
Additionally, businesses that deal with environmental concerns, such as waste management or pollution control, may require specific permits from the appropriate federal agencies.
Renewing and Updating Permits: Once you have obtained the necessary permits and licenses, be aware of their expiration dates. Many permits require renewal annually or at specific intervals. Stay organized and keep track of renewal dates to ensure ongoing compliance with state and local regulations.
Remember, this guide provides a general overview of the business permit requirements in Oklahoma. It is crucial to conduct thorough research and consult with relevant government agencies or professionals to ensure that you have obtained all the necessary permits for your specific business.
Starting a business can be a complex process, but by understanding and fulfilling the permit requirements, you can establish a solid foundation for your business in Oklahoma. Compliance with legal obligations not only demonstrates your commitment to operating ethically but also protects your business from potential penalties and legal issues.
Read Also: Unlock Your Potential with a Free Tax Preparation Course
Business Structure in Oklahoma

Establishing a successful business requires careful planning, and one crucial decision that entrepreneurs in Oklahoma must make is selecting the most suitable business structure. The business structure you choose will influence everything from legal obligations and taxation to personal liability and operational flexibility.
Sole Proprietorship: Sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common form of business structure. As a sole proprietor, you and your business are considered one entity. While this structure offers simplicity, it also means unlimited personal liability for any debts or obligations of the business. Registering a sole proprietorship in Oklahoma typically involves minimal formalities and allows for direct control and retention of all profits.
Partnership: Partnerships are formed when two or more individuals come together to carry out a business venture. In Oklahoma, there are two main types of partnerships: general partnerships (GPs) and limited partnerships (LPs).
GPs involve shared management and equal personal liability among partners, while LPs allow for limited partners who enjoy limited liability but have no management control. Partnerships in Oklahoma should ideally have a written partnership agreement that outlines rights, responsibilities, and profit-sharing arrangements.
Limited Liability Company (LLC): The Limited Liability Company (LLC) is a flexible business structure that combines elements of both partnerships and corporations. An LLC offers personal liability protection for its owners (referred to as members) and provides flexibility in management and taxation.
Oklahoma requires filing Articles of Organization with the Secretary of State to establish an LLC. It is worth noting that LLCs can be operated by a single member or have multiple members, offering versatility to suit various business sizes and needs.
Corporation: A corporation is a separate legal entity that exists independently of its owners (shareholders). Oklahoma recognizes two types of corporations: C corporations (C corps) and S corporations (S corps). C corporations have more flexibility in terms of ownership, issuing stocks, and attracting investors.
However, they are subject to double taxation—profits are taxed at both the corporate and individual levels. On the other hand, S corporations offer pass-through taxation, meaning profits and losses are reported on shareholders’ personal tax returns. S corps have specific eligibility criteria, such as a limit on the number of shareholders and restrictions on certain types of shareholders.
Nonprofit Corporation: Nonprofit corporations are formed for charitable, educational, religious, or other non-profit purposes. These entities must meet specific IRS requirements to obtain federal tax-exempt status.
In Oklahoma, nonprofits are formed by filing Articles of Incorporation with the Secretary of State and adhering to additional reporting obligations. Nonprofits rely on donations, grants, and fundraising to sustain their operations while being exempt from certain taxes.
Choosing the right business structure in Oklahoma is a pivotal step in laying a strong foundation for your venture. Each structure carries distinct advantages, disadvantages, and legal obligations.
Carefully evaluating factors such as personal liability, tax implications, management structure, and operational flexibility will help you make an informed decision.
It is advisable to consult with an attorney or a qualified business professional who can provide guidance tailored to your specific business goals and ensure compliance with Oklahoma’s regulations. Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the business landscape in Oklahoma and set your entrepreneurial dreams on the path to success.
Read Also: Check Out These Valuable Madame Alexander Dolls