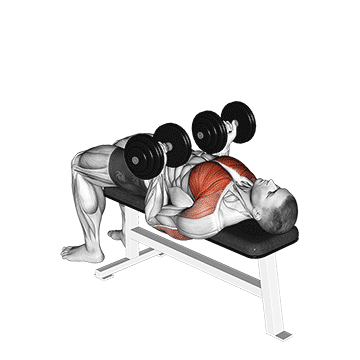
Let’s all delve into the world of the dumbbell chest press, a fundamental exercise that forms the cornerstone of any well-rounded strength training program.
The dumbbell chest press, also known as the dumbbell bench press, is a compound exercise targeting the muscles of the chest, shoulders, and triceps. It is a versatile and effective movement that can be adapted to various fitness levels and goals.
Execution
1. Set-Up: Begin by selecting an appropriate pair of dumbbells based on your fitness level. Sit on a flat bench with a dumbbell in each hand, positioned at shoulder height. Your feet should be firmly planted on the ground, and your back should be flat against the bench.
2. Grip: Hold the dumbbells with a neutral grip, palms facing forward. This grip engages the chest muscles more effectively while also recruiting the triceps and shoulders.
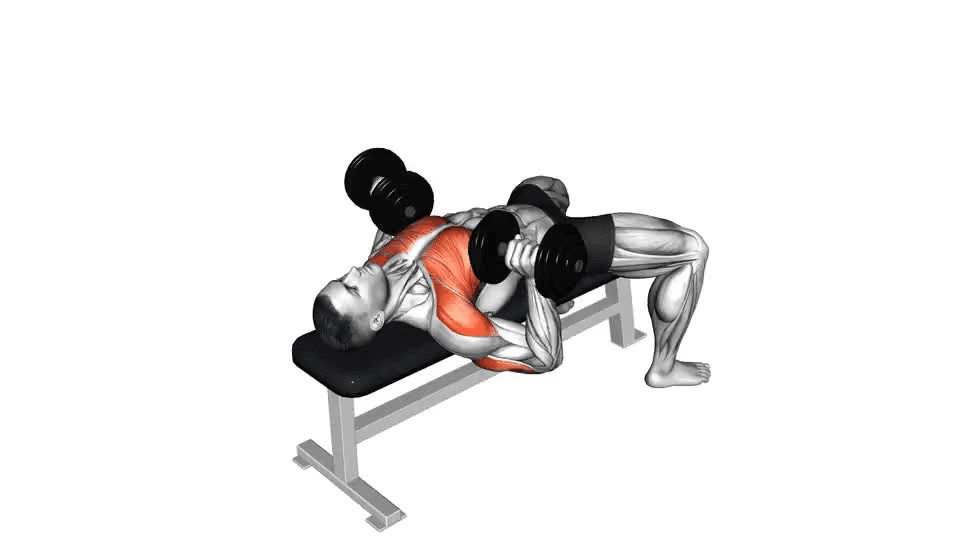
3. Movement: Lower the dumbbells to the sides of your chest, keeping your elbows at a 90-degree angle. Maintain control throughout the descent, avoiding any rapid or jerky movements. Press the dumbbells back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
4. Breathing: Inhale as you lower the dumbbells, and exhale as you press them back up. Proper breathing is crucial for maintaining stability and maximizing power during the exercise.
Benefits
1. Muscle Engagement: The dumbbell chest press engages the pectoral muscles, anterior deltoids, and triceps. This comprehensive activation promotes balanced upper body development.
2. Stability and Control: Unlike barbell presses, the dumbbell variation requires greater stabilization as each arm works independently. This enhances muscle coordination and helps address muscle imbalances.
3. Versatility: The exercise can be performed on various incline/decline benches to target different areas of the chest. This adaptability allows for a well-rounded chest development.
Common Mistakes and Tips
1. Excessive Arching: Avoid arching your back excessively. Maintain a natural arch and keep your core engaged for stability.
2. Rushing Repetitions: Focus on controlled movements rather than rushing through repetitions. This ensures proper muscle engagement and reduces the risk of injury.
3. Overloading: Start with a manageable weight to perfect your form. Gradually increase the weight as your strength improves.
Imagine you’re sculpting a statue – each repetition of the dumbbell chest press is like a chisel, carving definition into your chest muscles. Just as a sculptor pays attention to every detail, you must focus on the precision and control of each movement to achieve a masterpiece physique.
Progression and Variation
Once you’ve mastered the basic form of the dumbbell chest press, it’s time to explore progression and variation. These strategies not only keep your workouts interesting but also contribute to continuous muscle development.
1. Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the resistance or weight used during the dumbbell chest press to challenge your muscles and promote growth. This progressive overload stimulates the muscles to adapt and become stronger over time.
2. Incline and Decline Press: Experiment with different bench angles to target specific areas of the chest. Incline presses emphasize the upper chest, while decline presses focus on the lower chest. This variation adds depth to your training and promotes a well-balanced chest development.
3. Unilateral Training: Incorporate unilateral (single-arm) dumbbell presses to address any strength imbalances between your left and right sides. Unilateral training also engages stabilizing muscles, fostering better overall functional strength.
Read Also Why a Balanced Fitness Routine is Key to Long-Term Health and Wellness
Integration into Training Programs
1. Strength Phase: Include the dumbbell chest press in your strength-focused workouts, using lower rep ranges (around 6-8 reps) with heavier weights. This builds foundational strength and muscle mass.
2. Hypertrophy Phase: Shift to a moderate rep range (around 8-12 reps) to target muscle hypertrophy. Focus on a controlled eccentric phase (lowering the dumbbells) to maximize muscle tension and stimulate growth.
3. Endurance Phase: During endurance-focused phases, perform higher rep sets (around 12-15 reps) to enhance muscular endurance. This is beneficial for overall stamina and conditioning.
Common Questions
1. How often should I do the dumbbell chest press? Incorporate the dumbbell chest press 1-3 times per week, depending on your overall training volume and goals. Allow adequate rest between sessions to promote recovery.
2. Can beginners do the dumbbell chest press? Yes, beginners can start with lighter weights and focus on mastering proper form before gradually increasing resistance.
3. Is the dumbbell chest press suitable for women? Absolutely! The dumbbell chest press is a beneficial exercise for both men and women, contributing to upper body strength and aesthetics.
Safety Considerations
Before embarking on your dumbbell chest press journey, it’s crucial to prioritize safety. Here are some key considerations:
1. Warm-Up: Always begin your workout with a proper warm-up. Engage in dynamic stretches and light cardio to increase blood flow, flexibility, and prepare your muscles for the upcoming exercise.
2. Proper Form: Maintain strict form throughout the exercise. Avoid excessive arching of the back, and ensure your elbows are at a 90-degree angle during the descent. This not only maximizes effectiveness but minimizes the risk of injury.
3. Spotter (if needed): If lifting heavy, having a spotter can provide an extra layer of safety. They can assist you in case you reach failure during a set, preventing potential accidents.
4. Progress Gradually: Progression is key, but rushing into heavy weights can lead to injury. Gradually increase the resistance as your strength improves, allowing your muscles, tendons, and ligaments to adapt.
Tracking Progress
1. Keep a Workout Log: Documenting your workouts, including the weight lifted, sets, and repetitions, helps you track progress over time. This not only motivates you but also allows for strategic adjustments to your training program.
2. Performance Metrics: Pay attention to how the dumbbell chest press feels during each session. Are you finding it easier to lift a certain weight? Are you experiencing increased endurance? These subtle cues can provide valuable insights into your progress.
Real-Life Applications
Imagine you’re a parent lifting your child or groceries. The strength and stability developed through the dumbbell chest press directly translate to everyday tasks. Whether it’s carrying luggage, pushing a heavy door, or even engaging in recreational sports, the functional benefits extend far beyond the gym.
Integration with Other Exercises
1. Supersetting: Combine the dumbbell chest press with exercises that target different muscle groups, such as pull-ups or rows. This optimizes your workout time and promotes overall muscular balance.
2. Push-Pull Balance: Balance your chest-focused exercises with adequate back and posterior chain work. This not only prevents muscle imbalances but also contributes to a well-rounded physique.
Nutritional Support
Optimal results from your dumbbell chest press efforts also depend on a well-balanced diet. Ensure you’re consuming enough protein to support muscle repair and growth, along with a mix of carbohydrates and healthy fats for energy.
In summary, the dumbbell chest press is more than a mere exercise; it’s a journey of self-improvement and physical empowerment. By embracing proper form, progression, and a holistic approach to fitness, you’re not just building a strong chest , you’re cultivating a resilient and capable body that enhances your daily life.
So, let each repetition be a step toward a healthier, stronger, and more vibrant version of yourself. Happy lifting and stay committed to your fitness journey!