Before a marketer fixes a price, he should keep in mind certain basic considerations. The pricing policy he adopts is closely related to his other policies, like production programs, advertising policy, and selling methods.
For example, it may be necessary to reduce the price to offset the probable loss of sales from a lower advertising budget or to enable fuller utilization of plant capacity more quickly. Aggressive sales. a campaign may be necessary to meet the advent of a new competitor.
Read Also: Importance and Reasons for Branding
Your price should not be so high that it attracts others to compete with you. A low price may result in such a high volume of sales and low unit costs that profits are maximized even at low prices.
If a marketing manager is to make effective pricing decisions, he should be clear about the firm’s long-term marketing objectives for the entire range of products and services. If the firm is interested in increased market share, it would have to resort to penetration pricing.
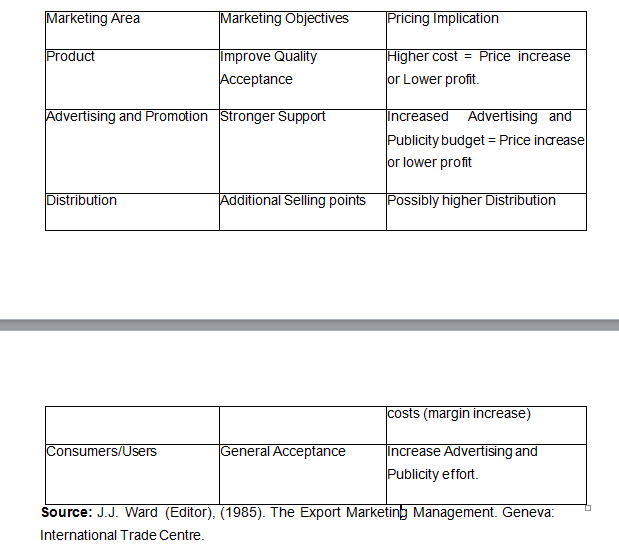
If it is interested in short-term profitability, it may have a higher price even at the expense of sales volume and market share. The following table gives a summary of some marketing objectives and their pricing implications:
Some Marketing Objectives & their Pricing Implications
Read Also: Methods of Segmenting Industrial and Business Markets (Market Segmentation)