What is assistive technology? It’s a question that opens the door to a world of possibilities—a world where technology becomes a guiding light for individuals facing various challenges. Assistive technology, often abbreviated as AT, is a collection of tools, devices, and services designed to make life more accessible for people with disabilities.
In its simplest form, assistive technology is a helping hand, empowering individuals to overcome barriers and engage more fully in daily activities.
The essence of assistive technology lies in its ability to enhance independence, whether through mobility aids, communication devices, or educational tools. From wheelchairs that provide newfound freedom of movement to communication devices that give voice to those who face speech challenges, assistive technology is a transformative force in the lives of many.
In this exploration, we’ll embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of assistive technology. We’ll go into its diverse categories, ranging from tools that aid mobility to devices fostering cognitive skills. As we navigate this landscape, we’ll also trace the historical evolution of assistive technology, witnessing how innovation has shaped its trajectory over the years.
Moreover, we’ll shine a light on the profound impact of assistive technology on daily life, examining how it influences education, employment, social inclusion, and independent living. Through a simple and informative lens, we’ll uncover the ways in which assistive technology acts as a catalyst for positive change.
Join us in this exploration of assistive technology—an exploration that goes beyond gadgets and gears. It’s a journey into a realm where technology becomes a bridge, connecting individuals with disabilities to a world of possibilities and breaking down barriers along the way.
Read also: The Challenge of Machines Understanding Text Data
What is Assistive Technology
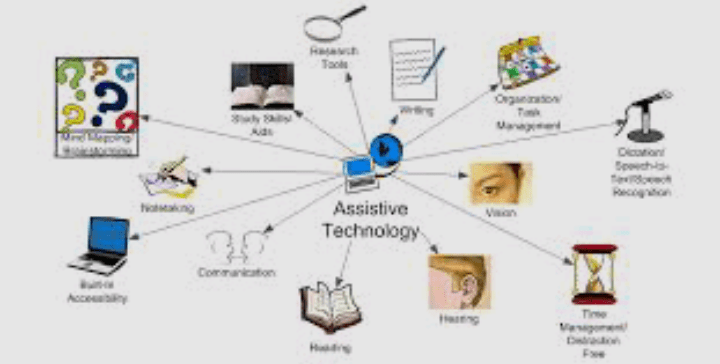
Defining Assistive Technology
At its core, assistive technology refers to any product, system, or service designed to enhance the functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities. This can include devices that aid in mobility, communication, education, and other daily activities. The primary goal of assistive technology is to break down barriers, allowing individuals with disabilities to engage more actively in society and pursue a life of greater autonomy.
Categories of Assistive Technology
1. Mobility Aids
Mobility aids are instrumental in enhancing the physical movement of individuals with disabilities. Wheelchairs, walkers, and scooters are common examples. Advancements in this category have led to the development of powered wheelchairs with sophisticated control systems, offering increased independence to users.
2. Communication Devices
For those with communication challenges, assistive technology provides tools to express thoughts and ideas effectively. Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices, ranging from simple picture boards to high-tech speech-generating devices, fall into this category. These devices play a pivotal role in empowering individuals with speech impairments.
3. Vision Enhancement Tools
Visually impaired individuals benefit from assistive technology designed to enhance their visual experiences. Screen readers, magnifiers, and Braille displays are key tools that bridge the gap, allowing access to information and fostering educational and vocational opportunities.
4. Hearing Aids and Communication Systems
Hearing aids are quintessential in the realm of assistive technology for individuals with hearing impairments. Additionally, communication systems like real-time text (RTT) and captioning services contribute to improved communication for deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals.
5. Educational and Learning Aids
Assistive technology has revolutionized education for individuals with disabilities. Text-to-speech software, voice recognition tools, and adaptive learning platforms cater to diverse learning needs, ensuring that everyone has equal access to educational resources.
6. Daily Living Aids
Devices designed to assist with daily activities, such as dressing, cooking, and personal hygiene, fall under this category. Adaptive tools like gripping aids, utensils with ergonomic designs, and specialized clothing make daily living more manageable for individuals with physical disabilities.
7. Cognitive Assistive Technology
For individuals with cognitive impairments, assistive technology offers solutions to enhance memory, organization, and cognitive skills. Apps and devices that provide reminders, prompts, and organizational support play a vital role in promoting independence in daily tasks.
8. Environmental Control Systems
These systems empower individuals with limited mobility to control their home environments. Through voice-activated commands or adaptive switches, users can manage lights, thermostats, and electronic devices, fostering a sense of autonomy within their living spaces.
Read also: Why It’s Essential Children Learn to Code
The Evolution of Assistive Technology
The roots of assistive technology can be traced back to the early 20th century, with the invention of devices aimed at supporting individuals with vision and hearing impairments. However, it was the post-World War II era that witnessed a significant surge in the development of assistive devices, driven by the need to rehabilitate injured veterans.
Advancements in electronics and computing in the latter half of the 20th century played a pivotal role in shaping assistive technology as we know it today. The advent of microprocessors and miniaturized components paved the way for more sophisticated and portable devices.
The 1980s and 1990s saw the emergence of personal computers and the integration of assistive technology into mainstream computing, opening new doors for individuals with disabilities.
The 21st century has witnessed an unprecedented acceleration in assistive technology innovation. The proliferation of smartphones and tablets, coupled with the rise of wearable devices, has ushered in a new era of accessibility. The development of more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces has further democratized access to assistive technology, making it more widely available and easier to use.
The Impact of Assistive Technology on Daily Life
1. Education and Employment
Assistive technology has been a game-changer in the realm of education and employment for individuals with disabilities. In educational settings, students with diverse needs can access information, participate in class activities, and demonstrate their knowledge using a variety of assistive tools. This not only levels the playing field but also empowers individuals to pursue higher education and professional opportunities.
In the workplace, assistive technology plays a crucial role in creating inclusive environments. Screen readers, voice recognition software, and adaptive keyboards enable individuals with disabilities to perform tasks effectively and contribute meaningfully to various industries. Employers are increasingly recognizing the value of diverse talents and are investing in assistive technology to create accessible workplaces.
2. Social Inclusion and Communication
One of the profound impacts of assistive technology is its role in fostering social inclusion. Communication devices, such as AAC devices and speech-generating devices, enable individuals with communication impairments to interact with their peers, family members, and the broader community. Social media platforms, equipped with accessibility features, further amplify the voices of individuals with disabilities, providing a platform for expression and connection.
3. Independent Living
Assistive technology contributes significantly to independent living by addressing various challenges faced by individuals with disabilities. Mobility aids, home automation systems, and adaptive tools for daily living empower users to navigate their homes and communities with greater autonomy. This not only enhances quality of life but also reduces dependence on caregivers, promoting a sense of self-reliance.
4. Recreation and Leisure
Advancements in assistive technology have extended to the realm of recreation and leisure, ensuring that individuals with disabilities can participate in a wide range of activities. Adaptive sports equipment, gaming consoles with accessibility features, and virtual reality experiences tailored for diverse needs are just a few examples of how technology is enriching the recreational experiences of individuals with disabilities.
Challenges and Future Directions
While assistive technology has made tremendous strides, challenges persist on the path to creating a fully inclusive society. Financial barriers often limit access to cutting-edge assistive devices, and there is a need for increased awareness and advocacy to address these disparities. Additionally, the rapid pace of technological advancement necessitates ongoing efforts to ensure that new innovations are inclusive and accessible from the outset.
The future of assistive technology holds exciting possibilities. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are poised to play a transformative role in creating more personalized and intuitive assistive solutions. The integration of sensor technologies, robotics, and brain-computer interfaces opens up new frontiers for enhancing the capabilities of assistive devices.
Read also: Biological Discs, Activated Sludge and Oxidation Pond Process
