What is blockchain technology? It’s a question that has sparked curiosity and conversations in tech circles and beyond. In its simplest form, blockchain is a revolutionary way of keeping records. But it’s not just about data; it’s about creating a secure and transparent digital environment that has the potential to transform the way we interact with information, assets, and each other.
At its core, blockchain is like a digital ledger – a shared, decentralized database that keeps track of transactions across a network of computers. The magic happens through a combination of decentralization, cryptography, and consensus mechanisms.
Unlike traditional databases, there’s no central authority in charge. Instead, every participant on the network has a copy of the entire ledger, and they work together to validate and record transactions in a tamper-proof way.
The journey of blockchain technology began with Bitcoin, a digital currency that introduced the concept of a blockchain as its underlying technology. However, the applications of blockchain extend far beyond cryptocurrencies. It’s a versatile tool with the potential to reshape industries, from finance and supply chain to healthcare and beyond.
As we embark on this exploration of blockchain, we’ll unravel the intricate workings of this technology, dissect its fundamental components, and examine the diverse range of applications that make it a key player in the ever-evolving landscape of innovation.
So, buckle up as we demystify the world of blockchain, bringing this transformative technology from the realm of tech jargon to a place where everyone can grasp its significance in shaping the digital future.
Read also: The Challenge of Machines Understanding Text Data
What is Blockchain Technology
1. Understanding the Basics
A. What is Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that facilitates secure and transparent record-keeping. Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a single entity controls and manages a database, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, allowing participants (nodes) to reach consensus on the state of the ledger.
B. The Genesis: Bitcoin and Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain technology gained prominence through its association with Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency introduced by an anonymous entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. Bitcoin’s blockchain serves as a public ledger for recording all transactions in a secure and tamper-resistant manner, ensuring transparency and immutability.
2. How Blockchain Works
A. Decentralization and Peer-to-Peer Networks
Decentralization lies at the heart of blockchain technology. In a blockchain network, each participant (node) maintains its copy of the entire ledger, ensuring redundancy and resilience. Peer-to-peer networks enable communication and collaboration among nodes, fostering a trustless environment.
B. Consensus Mechanisms
To maintain the integrity of the ledger, blockchain networks employ consensus mechanisms, which are protocols for achieving agreement among nodes. Common mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT). These mechanisms ensure that only valid transactions are added to the ledger.
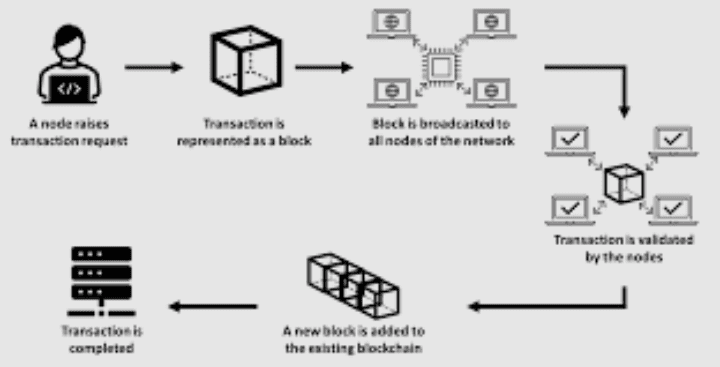
C. Blocks and Transactions
Blockchain transactions are grouped into blocks, with each block containing a reference to the previous block, forming a chain. This chaining of blocks ensures the chronological order and immutability of transactions. To add a new block to the chain, nodes must solve a complex mathematical puzzle, a process known as mining in PoW-based blockchains.
3. Key Components of Blockchain Technology
A. Cryptography
Cryptography is a fundamental component of blockchain, providing security and privacy to transactions. Public and private keys are used to encrypt and decrypt data, ensuring that only authorized parties can access and validate transactions.
B. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Operating on the blockchain, smart contracts automate and enforce the execution of contractual clauses, eliminating the need for intermediaries and enhancing efficiency.
Read also: Why It’s Essential Children Learn to Code
4. Applications of Blockchain Technology
A. Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets
While Bitcoin remains the most well-known application of blockchain, numerous cryptocurrencies and digital assets have emerged. Ethereum, for example, introduced the concept of smart contracts, expanding the utility of blockchain beyond simple peer-to-peer transactions.
B. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology offers transparent and traceable supply chain solutions. By recording every stage of a product’s journey on the blockchain, stakeholders can verify the authenticity, origin, and conditions of goods, reducing fraud and enhancing consumer trust.
C. Financial Services
The financial sector has embraced blockchain for its potential to revolutionize processes such as cross-border payments, remittances, and securities trading. Blockchain’s efficiency, transparency, and security can streamline financial transactions, reducing costs and processing times.
D. Healthcare
In healthcare, blockchain can enhance data security and interoperability. Patient records stored on a blockchain can be accessed securely by authorized parties, ensuring accurate and up-to-date medical information. This has the potential to improve patient care and streamline administrative processes.
E. Identity Management
Blockchain-based identity management solutions aim to provide individuals with greater control over their personal data. Users can manage and share their identity securely, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud.
F. Voting Systems
The transparency and security inherent in blockchain make it an appealing technology for developing secure and tamper-proof voting systems. Blockchain-based voting can enhance the integrity of electoral processes by preventing manipulation and ensuring accurate tallies.
5. Challenges and Considerations
A. Scalability
While blockchain technology offers numerous advantages, scalability remains a challenge. As the number of transactions increases, the capacity of some blockchain networks to handle the load may become a bottleneck. Ongoing research and development aim to address scalability issues and enhance blockchain’s capacity.
B. Regulatory Concerns
The decentralized and pseudonymous nature of blockchain transactions has raised regulatory concerns related to fraud, money laundering, and tax evasion. Governments and regulatory bodies are actively exploring ways to strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring compliance with existing laws.
C. Energy Consumption
Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, employed by some blockchains like Bitcoin, require substantial computational power and energy consumption for mining. This has led to environmental concerns, prompting exploration of alternative consensus mechanisms with lower environmental impact, such as Proof of Stake (PoS).
6. Future Trends and Developments
A. Interoperability
Interoperability, the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate and share data seamlessly, is a key focus of ongoing research and development. Establishing standards for interoperability can unlock new possibilities for cross-chain collaborations and enhance the overall utility of blockchain technology.
B. Integration with Internet of Things (IoT)
The integration of blockchain technology with the Internet of Things (IoT) holds the potential to create a secure and transparent ecosystem for connected devices. Blockchain can ensure the integrity of data generated by IoT devices and enable secure transactions within the IoT network.
C. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Several central banks are exploring the concept of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), leveraging blockchain technology to issue digital currencies. CBDCs aim to enhance financial inclusion, reduce transaction costs, and provide central banks with more effective tools for monetary policy.
D. Quantum Computing and Security
As quantum computing advances, concerns arise regarding the potential threat it poses to traditional cryptographic algorithms used in blockchain. Research is ongoing to develop quantum-resistant cryptographic solutions, ensuring the continued security of blockchain networks.
Read also: Waste To Fertilizer: What You Need to Know