Today we delve into the world of push-pull workout, a highly effective and well-balanced approach to resistance training. This method is designed to target specific muscle groups while promoting overall strength and symmetry.
Whether you’re a seasoned fitness enthusiast or just starting your fitness journey, understanding the principles of push-pull workouts can elevate your training routine to new heights.
Push-Pull Concept
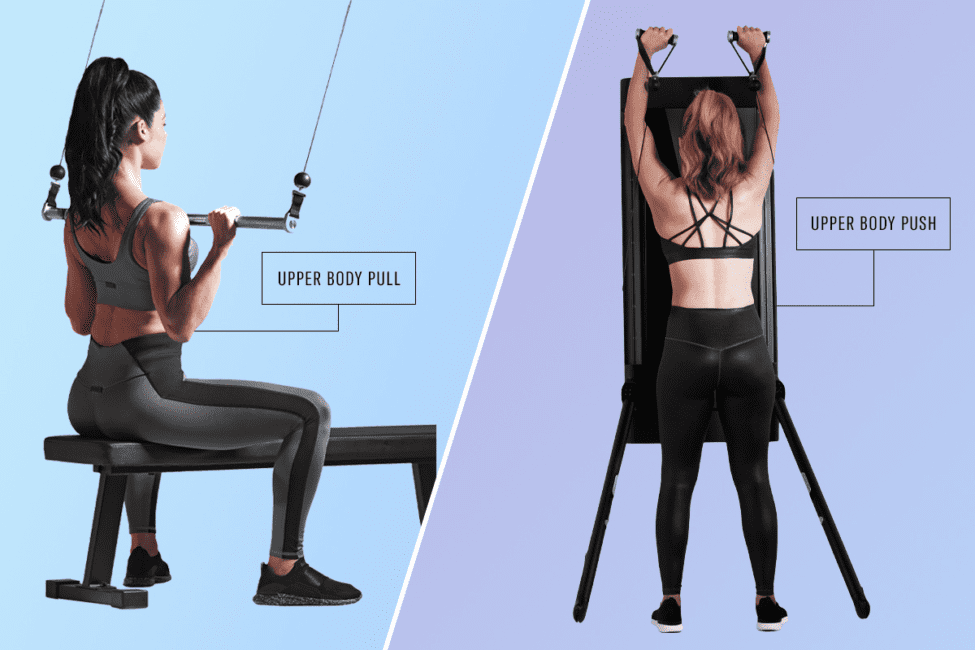
The push-pull workout revolves around the fundamental concept of dividing exercises into two main categories: pushing movements and pulling movements. This classification is based on the direction of force applied during the exercise.
1. Pushing Movements:
Pushing movements involve exerting force away from your body. This primarily targets muscles involved in extending or pushing motions, such as the chest, shoulders, and triceps. Classic examples of pushing exercises include:
1. Bench Press: This compound movement engages the chest, shoulders, and triceps. It’s a cornerstone exercise for building upper body strength.
2. Shoulder Press: Focusing on the deltoids, this exercise enhances shoulder strength and stability.
3. Tricep Dips: Isolating the triceps, this bodyweight exercise complements weighted pushing movements.
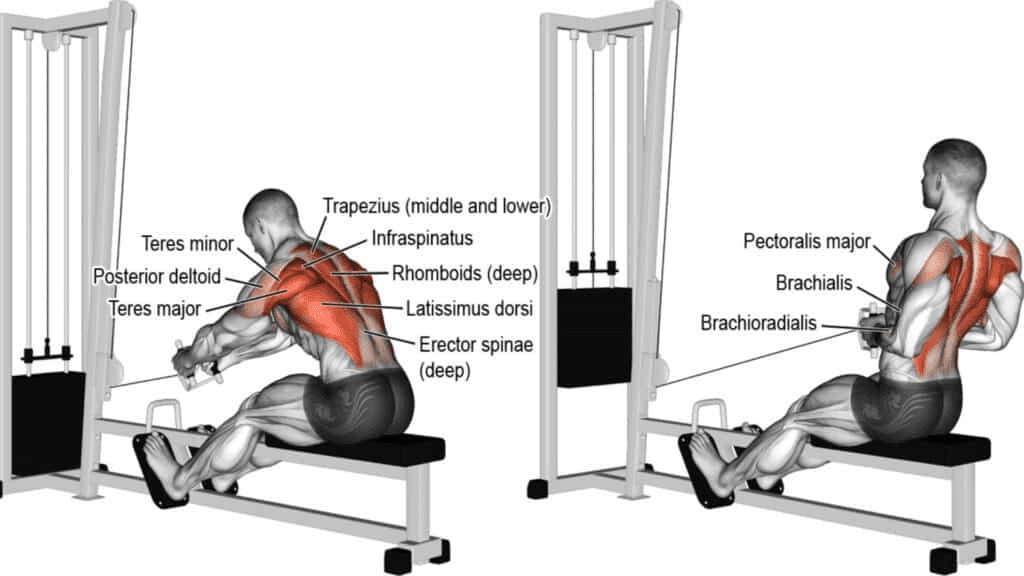
2. Pulling Movements:
Pulling movements, on the other hand, involve bringing resistance towards your body, targeting muscles involved in pulling or contracting motions. Muscles worked include the back, biceps, and rear deltoids. Notable pulling exercises include:
1. Pull-Ups/Chin-Ups: These compound exercises engage the upper back, lats, and biceps, promoting upper body pulling strength.
2. Barbell Rows: A key exercise for developing a strong and well-defined back, targeting the lats and rhomboids.
3. Face Pulls: Isolating the rear deltoids and upper back, face pulls contribute to shoulder health and posture.
Benefits of Push-Pull Workouts
1. Muscle Balance: By alternating between push and pull exercises, you ensure that opposing muscle groups receive equal attention. This helps prevent muscular imbalances and enhances overall aesthetics.
2. Efficient Workouts: Push-pull routines are time-efficient, allowing you to target multiple muscle groups in a single session. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with busy schedules.
3. Enhanced Recovery: As different muscle groups are worked on different days, adequate recovery time is provided for each area. This minimizes the risk of overtraining and reduces the likelihood of injuries.
Sample Push-Pull Workout Split
Here’s an example of a push-pull workout split for a three-day-per-week routine:
Day 1: Push (Upper Body)
1. Bench Press: 4 sets x 8-10 reps
2. Shoulder Press: 3 sets x 10-12 reps
3. Tricep Dips: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
4. Lateral Raises: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
Day 2: Pull (Upper Body)
1. Pull-Ups: 4 sets x max reps
2. Barbell Rows: 3 sets x 10-12 reps
3. Face Pulls: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
4. Bicep Curls: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
Day 3:
1. Rest or active recovery
Day 4: Push (Lower Body)
1. Squats: 4 sets x 8-10 reps
2. Leg Press: 3 sets x 10-12 reps
3. Leg Extensions: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
4. Calf Raises: 3 sets x 15-20 reps
Day 5: Pull (Lower Body)
1. Deadlifts: 4 sets x 8-10 reps
2. Romanian Deadlifts: 3 sets x 10-12 reps
3. Hamstring Curls: 3 sets x 12-15 reps
4. Seated Calf Raises: 3 sets x 15-20 reps
Day 6-7:
1. Rest or active recovery
Read Also Difference Between Health and Fitness
Advanced Techniques and Variations
For those looking to add complexity and variety to their push-pull routine, advanced techniques and exercise variations can be incorporated. Here are a few options to consider:
1. Supersets and Tri-Sets: Combine complementary push and pull exercises in a superset or tri-set fashion. For example, pair bench presses with bent-over rows or shoulder presses with pull-ups. This approach increases workout intensity and efficiency.
2. Drop Sets: Perform a set of an exercise to failure, then reduce the weight and continue with additional reps. This technique helps to push muscles to their limits, promoting muscle hypertrophy and endurance.
3. Incorporate Unilateral Movements: Integrate single-limb exercises such as single-arm dumbbell presses or single-leg Romanian deadlifts. Unilateral movements address muscle imbalances, enhance stability, and activate smaller stabilizing muscles.
4. Functional Movements: Include functional movements that mimic real-world activities. For instance, incorporate medicine ball throws or cable wood chops, engaging multiple muscle groups and enhancing overall athleticism.
5. Periodic Intensity Cycling: Cycle through periods of higher and lower intensity in your training. This could involve incorporating a week of high-intensity training followed by a week of lower-intensity or active recovery. This approach helps prevent burnout and keeps your body responsive to training stimuli.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Ignoring Proper Form: Always prioritize proper form over lifting heavier weights. Incorrect form not only reduces the effectiveness of the exercise but also increases the risk of injury.
2. Neglecting Warm-Up and Cool Down: Skipping warm-up and cool-down routines can hinder performance and increase the likelihood of injury. Allocate sufficient time for both to optimize your workouts and enhance recovery.
3. Overlooking Progressive Overload: Without progressive overload, your muscles won’t be adequately stimulated for growth. Gradually increase the intensity of your workouts to promote continuous progress.
4. Insufficient Recovery: Recovery is just as crucial as the workout itself. Neglecting proper sleep, nutrition, and rest can impede progress and increase the risk of overtraining.
Periodization and Long-Term Planning
To ensure sustained progress and prevent training plateaus, consider incorporating periodization into your long-term planning. Periodization involves organizing your training into distinct phases, each with specific goals and varying intensity.
This approach helps to systematically manipulate training variables, promoting continuous adaptation and minimizing the risk of burnout or overtraining.
1. Hypertrophy Phase: Focus on higher rep ranges (8-12 reps) and moderate weights to induce muscle hypertrophy. This phase is essential for building muscle size and endurance.
2. Strength Phase: Transition to lower rep ranges (4-6 reps) with heavier weights. This phase emphasizes neuromuscular adaptations, increasing your ability to lift heavier loads.
3. Power Phase: Incorporate explosive movements, such as plyometrics or dynamic exercises, to enhance power and speed. This phase helps bridge the gap between strength and functional athleticism.
4. Active Recovery Phase: Integrate periods of lower intensity and active recovery, focusing on flexibility, mobility, and lighter exercises. This phase allows your body to recuperate, reducing the risk of overtraining.
By cycling through these phases strategically, you create a structured and progressive approach to your push-pull workouts, ensuring long-term success and minimizing the risk of burnout.
Tracking and Monitoring
Effectively tracking your workouts is crucial for gauging progress and making informed adjustments to your training plan. Keep a detailed log of your exercises, sets, reps, and weights used.
This not only provides a sense of accomplishment but also allows you to identify patterns, strengths, and areas that may require additional attention.
Consider incorporating performance metrics such as increased weight lifted, improved repetitions, or reduced rest times. Regularly reassess your fitness goals and make adjustments to your workout routine based on your evolving strengths and weaknesses.
Conclusion
Incorporating advanced strategies like periodization and careful tracking into your push-pull workout routine can take your fitness journey to the next level.
By embracing a holistic approach to training, including strength, hypertrophy, power, and active recovery phases, you ensure a well-rounded and sustainable progression towards your fitness goals.
Always prioritize your body’s signals, adjust your training plan as needed, and consult with fitness professionals for personalized guidance. Remember, the journey is as important as the destination, and with dedication and smart planning, you can achieve lasting success in your push-pull workouts.
Read Also 18 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Maytenus krukovii (Chuchuhuasi)